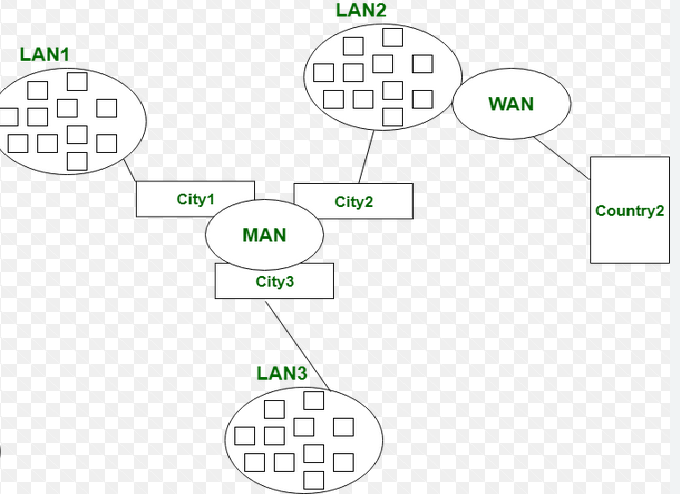
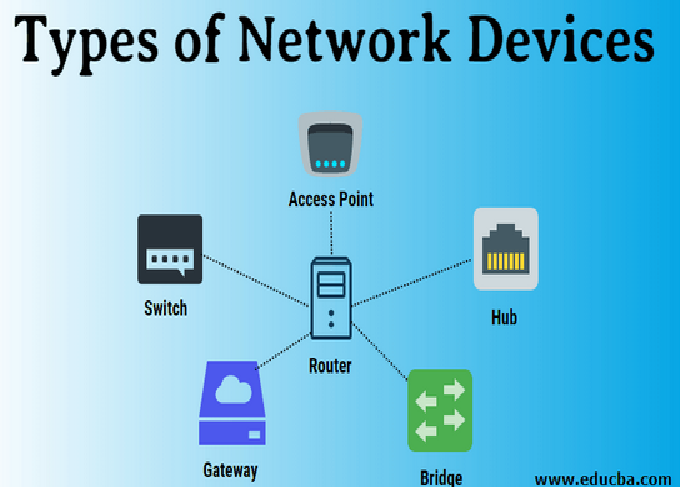
In the world of computer networking, communication between devices plays a vital role in data sharing, resource utilization, and collaboration. Networks allow computers to connect and exchange information seamlessly, whether within a small home office or across global corporations. Among the different types of networks, LAN (Local Area Network), MAN (Metropolitan Area Network), and WAN (Wide Area Network) are the most commonly discussed.
Although they all serve the same fundamental purpose — connecting devices — they differ in scale, technology, speed, ownership, and usage. Understanding these differences helps IT professionals and organizations choose the right type of network for their specific needs.
This article explains the differences between LAN, WAN, and MAN in simple terms, with examples and detailed comparisons to help you understand how each one works and where they are used.
What is a LAN (Local Area Network)?
A LAN (Local Area Network) is a small-scale network that connects computers and devices within a limited geographical area such as a home, school, office, or building. LANs are typically used to share resources like printers, files, and internet connections among multiple devices.
LANs are known for their high speed, low latency, and private ownership — meaning they are usually managed and maintained by the organization or individual who owns them.
Characteristics of LAN
-
Limited Area Coverage:
LANs cover a small geographical area, generally within a few hundred meters. Examples include home Wi-Fi networks or office Ethernet connections. -
High Data Transfer Speed:
Modern LANs can provide speeds ranging from 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps or more, depending on the infrastructure and equipment used. -
Low Setup Cost:
Because they cover small areas, LANs require less cabling and equipment, making them cheaper to install and maintain compared to larger networks. -
Private Ownership:
The organization or user owns and controls the LAN, meaning no external provider is required to operate it. -
Uses Ethernet and Wi-Fi:
Most LANs use Ethernet cables (wired) or Wi-Fi (wireless) to connect devices.
Examples of LAN
-
A home network connecting a few laptops, a smart TV, and a Wi-Fi router.
-
A small office network with multiple PCs connected to a central server and printer.
-
A school computer lab where all computers share files and internet access.
Advantages of LAN
-
High speed communication between connected devices.
-
Secure and easy to manage, since ownership is local.
-
Resource sharing reduces cost (e.g., shared printers and files).
-
Centralized data storage allows easy backup and monitoring.
Disadvantages of LAN
-
Limited to a small area.
-
Network management may require IT knowledge.
-
Can become crowded if too many devices are connected.
-
Hardware failure (e.g., router or switch) can disrupt the entire network.
What is a MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)?
A MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) is a type of network that spans a city or metropolitan area. It connects multiple LANs across various locations within the same region, enabling organizations to share data and resources across branches located in different parts of a city.
MANs are larger than LANs but smaller than WANs. They are often managed by service providers or government organizations that supply connectivity to multiple users within the same area.
Characteristics of MAN
-
Covers a City or Large Area:
A MAN can cover several kilometers — for instance, connecting multiple office buildings in different parts of the same city. -
Moderate Speed:
Speeds are generally lower than LAN but higher than most WANs, typically in the range of 100 Mbps to several Gbps. -
Public or Private Ownership:
MANs can be owned by organizations or maintained by internet service providers (ISPs) for public use. -
Uses Fiber Optic or Wireless Connections:
MANs often use fiber optic cables or microwave links to connect multiple LANs. -
Intermediate Scale:
It acts as a middle layer between LAN and WAN in terms of both size and complexity.
Examples of MAN
-
A city’s university network connecting different campus buildings located across town.
-
A government network connecting multiple municipal offices in one city.
-
A bank network connecting all its branches within a metropolitan area.
Advantages of MAN
-
Efficient connectivity across large areas such as cities.
-
Faster data sharing compared to WAN.
-
Cost-effective for organizations with multiple branches in one area.
-
Can serve as a backbone connecting multiple LANs.
Disadvantages of MAN
-
More expensive than LAN due to long-distance cabling.
-
Maintenance and troubleshooting require more expertise.
-
Security risks increase as more users share the network.
-
Limited to metropolitan or city boundaries.
What is a WAN (Wide Area Network)?
A WAN (Wide Area Network) is the largest type of computer network, covering countries, continents, or even the entire world. WANs connect multiple LANs and MANs using long-distance communication links such as fiber optics, satellites, and undersea cables.
The internet is the most common and well-known example of a WAN.
WANs are typically maintained by telecommunication companies, ISPs, or governments, and used by organizations to connect their geographically separated branches.
Characteristics of WAN
-
Extensive Area Coverage:
WANs span large geographical distances — from one city to multiple countries or continents. -
Lower Data Speeds Compared to LAN:
Although WAN speeds have improved, they still tend to be slower due to distance and routing complexities. -
Public or Private Ownership:
WAN infrastructure is usually owned and managed by ISPs or telecom providers, not by the end user. -
Use of Long-Distance Media:
WANs use satellite links, leased telephone lines, and fiber optic cables for connectivity. -
High Setup and Maintenance Cost:
WANs require expensive infrastructure and professional maintenance.
Examples of WAN
-
The Internet — a global network connecting millions of devices worldwide.
-
A multinational company’s network linking offices across different countries.
-
Banking networks that connect ATMs and branches nationwide.
Advantages of WAN
-
Global reach, enabling communication across countries.
-
Facilitates data sharing and remote collaboration for large organizations.
-
Allows centralized systems like cloud services and online databases.
-
Reliable communication for multinational corporations.
Disadvantages of WAN
-
High cost of setup and maintenance.
-
Slower speeds and higher latency than LAN or MAN.
-
Security threats, as data travels across public networks.
-
Complex configuration and reliance on external service providers.
Key Differences Between LAN, MAN, and WAN
| Feature | LAN (Local Area Network) | MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) | WAN (Wide Area Network) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Local Area Network | Metropolitan Area Network | Wide Area Network |
| Coverage Area | Small area (building, campus) | City or metropolitan area | Country or worldwide |
| Ownership | Private | Private or public | Public or private |
| Speed | Very high (up to 10 Gbps) | Moderate to high | Relatively lower |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High |
| Setup | Easy | Moderate | Complex |
| Data Transfer | Fast | Moderate | Slower due to distance |
| Security | High (private control) | Moderate | Low (public networks) |
| Example | Home network, school lab | City university network | Internet, global bank network |
Comparison Example: A Real-World Scenario
Imagine a large organization like a bank with multiple offices:
-
Head Office: Located in Lahore.
-
Branch Offices: In Faisalabad, Karachi, and Islamabad.
-
ATM Machines: Spread across Pakistan.
Here’s how LAN, MAN, and WAN would apply:
-
LAN: Each individual office (e.g., Lahore head office) has its own LAN connecting computers, servers, and printers locally.
-
MAN: The Lahore branch may use a MAN to connect its head office with other bank buildings within the same city.
-
WAN: The entire bank uses a WAN to connect all its branches and ATMs across Pakistan and beyond, enabling real-time transactions.
This combination allows efficient local communication (via LAN), city-wide connection (via MAN), and nationwide/global communication (via WAN).
Technologies Used in LAN, MAN, and WAN
-
LAN Technologies:
-
Ethernet (IEEE 802.3)
-
Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11)
-
Switches, routers, and access points
-
-
MAN Technologies:
-
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI)
-
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
-
Metro Ethernet
-
Wireless MAN (WiMAX)
-
-
WAN Technologies:
-
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
-
Satellite Communication
-
Leased Lines
-
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
-
SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN)
-
Security in LAN, MAN, and WAN
-
LAN Security: Easier to secure because it’s locally controlled. Techniques include firewalls, antivirus, and access control lists (ACLs).
-
MAN Security: Requires encryption and network segmentation due to multiple connected LANs and broader access.
-
WAN Security: Needs advanced security like VPNs, intrusion detection systems (IDS), encryption (SSL/TLS), and firewalls to protect data traveling over public networks.
Performance Considerations
-
Latency: LANs have the lowest latency because devices are nearby. MANs have slightly higher latency, and WANs experience the most due to long distances.
-
Bandwidth: LANs offer the highest bandwidth; WANs typically have lower bandwidth due to cost and distance.
-
Reliability: LANs are highly reliable; WANs depend on multiple external systems and links, so they’re more prone to disruptions.
Ownership and Maintenance
-
LANs are managed by internal IT teams.
-
MANs may be managed by either private organizations or ISPs.
-
WANs are mostly maintained by telecom providers and global ISPs, requiring contractual agreements.
When to Use LAN, MAN, or WAN
-
Use LAN when you need to connect computers within a single location — ideal for small businesses, schools, or home offices.
-
Use MAN when your organization has multiple offices in one city and needs high-speed interconnectivity.
-
Use WAN when your business operates across multiple cities or countries and requires seamless global connectivity.
The Future of Networking: LAN, MAN, and WAN in 2025 and Beyond
With the evolution of networking technologies, the boundaries between LAN, MAN, and WAN are becoming less distinct. Emerging technologies such as 5G, fiber-optic networks, cloud computing, and SD-WAN are reshaping how networks operate.
-
LANs are getting faster with Wi-Fi 7 and Gigabit Ethernet, supporting more IoT devices.
-
MANs are evolving into smart city networks, connecting public services, surveillance systems, and transportation.
-
WANs are integrating with cloud-based solutions, offering secure and efficient global connectivity through SD-WAN and AI-driven network management.
Conclusion
LAN, MAN, and WAN are the three foundational types of computer networks that differ mainly in size, speed, ownership, and technology.
-
LAN connects devices locally within homes or offices.
-
MAN connects networks within a city.
-
WAN links multiple cities or countries across vast distances.
Each has its own advantages and is suitable for different needs. While LAN offers high-speed, low-cost communication, MAN provides efficient city-wide connections, and WAN enables global connectivity.
Understanding these differences helps individuals, businesses, and IT professionals design efficient, secure, and scalable network infrastructures that match their communication requirements in today’s interconnected digital world.